What is Capacity Planning and why is critical for business performance?

How is capacity planning connected with business performance? Every organization aims to be efficient. And this efficiency can be measured in several ways:
- Higher success rate of projects and programs.
- A higher ROI from their project or product portfolios.
- Or higher productivity of the organization’s teams and staff.
Capacity planning is the process by which organizations will be able to evaluate whether they have the necessary resources to cope with all incoming demand and allocate capacity in different initiatives according to the organization´s priorities. A process that, if well designed, executed and monitored, will help companies to be more efficient and better prepared to address the most relevant initiatives.
In this post, we will explain what capacity planning is and how this process fits into Resource Management and Project Portfolio Management. We also detail best practices to follow, and the main advantages and disadvantages that organizations may face depending on whether or not they have correctly implemented their capacity planning processes.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is capacity planning?
- Capacity Planning goals.
- Types of capacity planning.
- What´s the role of capacity planning in Project Portfolio Management and Resource Management?
- Capacity Planning key concepts.
- Steps to follow to implement the capacity planning process.
- Capacity planning challenges.
- Advantages of Capacity Planning.
- Capacity planning best practices.
- Capacity planning examples in a PPM software.
- Conclusion.
What is capacity planning?
Capacity planning is the process by which an organization estimates whether it has the necessary resources to meet all incoming demand over a given period of time, and attribute capacity in the different initiatives according to business priorities.
We are in an era of change. Organizations are compelled to deal with a higher volume of incoming demand. Such is the number of requests received that most of them cannot meet them all without affecting their budget and performance. Or they fail to forecast the capacity they will need because they plan a year ahead, not 3 or 6 months ahead as required in today’s changing environment.
Capacity planning goals
And this is where capacity planning comes into play. It is a key process to optimize Demand Management and Resource Management because, if well implemented, it will help organizations to:
- Determine if you have the resources and skills to handle the volume of work in the coming months.
- Prioritize or postpone projects and initiatives depending on whether the company has the skills to undertake them successfully.
Broadly speaking, these are the capacity planning goals:
- Avoid resource shortage issues when undertaking projects and programs that are strategic for the business.
- Ensure that the organization has all the necessary skills to successfully manage its product and project portfolios.
- Avoid work environments where there is overcapacity and duplicated resources and skills.
Capacity planning avoids issues of shortage or excess of resources and competencies
Capacity planning, therefore, requires a detailed estimate of both the organization’s current capacity and future capacity based on demand. And, based on this forecast (which should be made every 3 to 6 months), to set up capacity planning processes to ensure that the necessary resources are available when they are needed.
Types of capacity planning
While in this post we are focusing on capacity planning as the process in which organizations estimate whether they have (and will have) the workforce and skills needed to meet demand, it is not the only type of capacity planning out there.
We can list 3 types of capacity planning, which are as follows:
- Workforce capacity planning. As already explained, it refers to having the necessary human capacity to meet the incoming demand in a satisfactory manner for a given period of time. It is a process by which organizations can decide to hire more staff, reduce headcount or reallocate resources to other roles where they will be more productive.
- Tool capacity planning: It means having the necessary tools and equipment to deliver the job. Depending on the sector, this may be computer equipment, machinery, transportation, software, tools, etc.
- Product capacity planning is the process through which a business estimates whether it will have an adequate amount of products and resources to meet demand. For instance, in the case of a large retail company, it involves ensuring there is sufficient stock in stores to meet the demand, as well as an adequate number of cashiers, POS systems, and other necessary resources.
Therefore, we are going to focus exclusively on workforce capacity planning and how this process is integrated into Project Portfolio Management and Resource Management.
What’s the role of capacity planning in Project Portfolio Management and Resource Management?
Capacity planning is of vital importance for efficient Project Portfolio Management. And also, one of the most challenging. The greater the volume of projects and programs to manage, the more complex it becomes to allocate resources to these projects.
The greater the number of projects to manage, the more complex the allocation of resources
See the Triskell platform in action in a personal demo
Moreover, if an organization does not have the resources and skills necessary to undertake the initiatives with the highest impact on its strategy, the impact can be catastrophic, as you can imagine.
Think about it for a moment from your perspective as PMO Manager. If for a project manager, the process of resource allocation for a particular project might by itself be a source of conflict with the managers of the different departments, this is getting worse as the PMO has a greater volume of initiatives to handle.
How can capacity planning help Project Portfolio Management and Resource Management? If you have processes in place to estimate your capacity with respect to incoming demand and analyze different possible scenarios within the organization, capacity planning will serve to:
- Allocate the right skills and resources to the relevant projects and programs to improve their performance.
- Ensure that strategic initiatives for the organization have the most appropriate and valuable organizational resources allocated to them.
- Hire new staff or train the current ones depending on whether you need to improve certain skills to successfully carry out certain initiatives.
- Prioritize or put projects on hold if a shortage of resources or skills to successfully undertake them is detected.
- To reallocate resources in a more agile manner in case of unexpected changes in the volume of demand or strategic objectives change.
Capacity planning key concepts
As you can see, capacity planning is critical for optimizing the performance of your business. But before we delve into the details, let’s first clarify some concepts and processes related to capacity planning. Although these concepts are often misunderstood, you will see that they are fundamentally interconnected.
Resource Management vs Capacity Planning
- Resource Management: These are processes at the project or program level to ensure the selection and allocation of appropriate resources to relevant projects and programs.
- Capacity Planning: it’s a process that is located at a more strategic level and is intended to ensure that a business has the resources and skills necessary to meet incoming demand for a given period.
- How do they interact with each other? Capacity planning is one layer above Resource Management. The better defined an organization’s capacity (total available resources and skills) is, the easier it is for project managers to plan for resource allocation and use.
Capacity Planning vs Resource Planning
- Resource Planning: this is the decision-making process by which an organization plans in the short and medium term the resources that will be allocated to certain projects and/or programs.
- Capacity Planning seeks to balance available resources and skills with incoming demand so that the organization’s performance does not suffer.
- How do they interact with each other? As with Resource Management, Capacity Planning is a step above. If there are no efficient capacity planning processes in place, problems will arise when planning resources for each project or program in the form of unqualified or overworked personnel being assigned.
Demand Planning vs Capacity Planning
- Demand Planning is a process by which an organization can predict in advance the demand for new projects, products or services from its customer and user base.
- Capacity Planning is made by processes by which you estimate the resources and skills needed to meet incoming demand over a defined timeframe.
- How do they interact with each other? Both processes need each other to be efficient. Without proper demand planning, it is impossible to estimate the resources and skills that will be needed to successfully meet the demand.
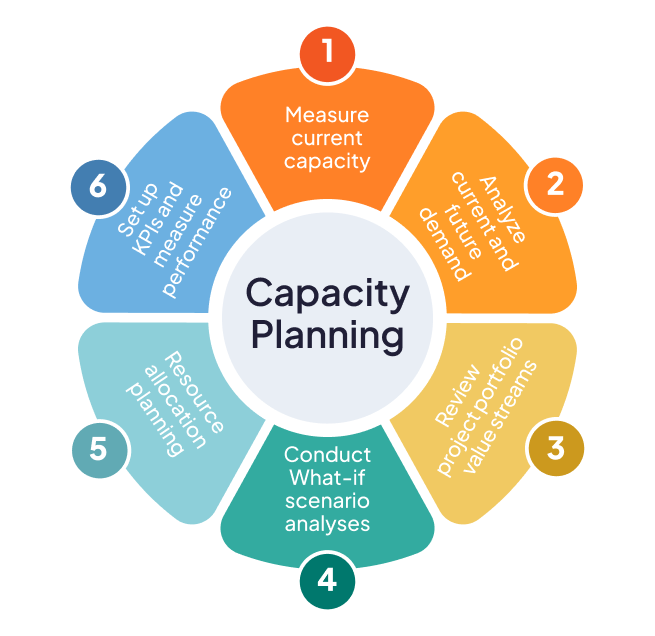
Steps to follow to implement the capacity planning process
Before capacity planning can help improve the performance of Project Portfolio Management or Resource Management, it is necessary to design a process. A process that should focus on the continuous improvement of mechanisms for assessing existing capacity and estimating future demand, as well as key performance indicators with which to monitor how well or poorly the process is performing.
These are the steps to follow to implement a capacity planning process:
- Calculate current capacity.
- Analyze current and future demand.
- Review the value streams of the organization’s project and product portfolios.
- Use tools with what-if scenario analysis features
- Plan resource allocation.
- Establish KPIs to measure the efficiency of our capacity planning process.
Each of the steps for implementing a capacity planning process are explained below.
1. Calculate current capacity
This step must be carried out meticulously so that the rest of the process goes smoothly. Here it is not only about listing the total resources available in each department of the organization, but it is also about going one step further. This report should also include, if possible, the following information:
- Current use of resources: are they also working on other projects in addition to doing their daily tasks? How much time do they dedicate to each task?
- The contractual relationship of the resources with the organization.
- A summary of the professional background and skills that each resource and department has.
2. Analyze current and future demand
Next, the current demand should be analyzed. This analysis should include:
- Priority and strategic relevance of each of the projects and initiatives the company is working on.
- The number of resources allocated to each initiative and the total hours that each resource dedicates.
- Budget and costs of each program and portfolio.
- Skills required to successfully complete each program and portfolio.
- Estimated start and end date of each program and portfolio.
Once the current demand has been listed, it is important to make an estimate of how the company’s demand will be in 3 to 6 months’ time. To do this, it will be important to use other data apart from those extracted from the current demand report to make an estimate as accurate as possible.
- Data history: Comparing different periods will help you to obtain quantitative data and trends on the evolution of incoming demand requests in the organization.
- Internal factors of the organization: this internal context can help you anticipate whether incoming demand will increase. For example, if management decides to develop a new product line or accelerate the company’s transformation process, it is expected that the volume of demand will increase.
- External factors: multiple external factors can affect the trend in incoming demand and the business performance itself. An economic recession, the emergence of new competitors or, as we have recently experienced, a pandemic can affect the evolution of incoming demand.
3. Review the value streams of the organization’s project and product portfolios
After having analyzed the organization’s capacity and its current and future demand, it is important to review the value streams of each of its project and product portfolios.
A value stream is all the steps demand must go through until it materializes into value for both customers and the business.
In view of the capacity planning process, this analysis has several purposes:
- List all departments and areas involved in the value stream of each portfolio.
- Identify the type of resources and skills required to generate value at each stage of the value stream.
- Detect areas of improvement and skills to be covered to optimize the continuous generation of value.
4. Use tools with what-if scenario analysis features
Next, and as a preliminary step to resource allocation planning, it is interesting to analyze the different scenarios in which the organization may find itself. This analysis must be carried out based on the historical data and the analysis of the internal and external factors discussed earlier in the second step.
Most of the best PPM software has functionalities for what-if Scenario Simulation. This scenario analysis will provide you with valuable insights for more efficient capacity planning. For example, it will help you determine which project portfolios should be prioritized according to each situation and, therefore, which type of resources should be given higher priority.
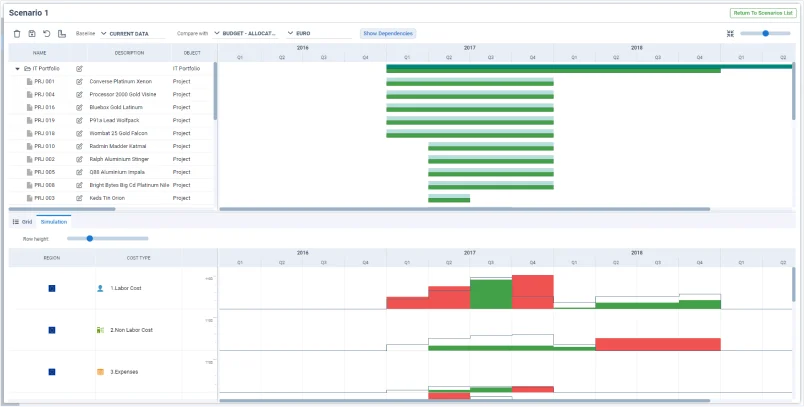
5. Plan resource allocation
Once the different scenarios have been analyzed in advance, resource allocation planning will be much more agile and efficient. For each scenario, you will have well-defined the organization’s priorities for each of its project portfolios, and the allocation of resources will be more in line with reality.
If the above steps have been properly carried out, then resource allocation can be planned much further in advance. Your organization will also gain in adaptability to make changes. And, whatever the scenario, resource allocation and capacity planning will be aligned with the strategic objectives at the time.
6. Establish KPIs to measure the efficiency of our capacity planning process
Once we have defined the capacity planning process, it is important to measure and monitor its performance. To do this, it is necessary to establish key performance indicators for the process to evaluate its performance and identify possible improvements.
There are many metrics you can use to measure this process. These are just a few KPI examples to measure capacity planning:
- Incidents due to capacity shortages. With this metric, we can quantify the number of projects or programs that have had to be put on hold due to the absence of the resources or skills necessary for their proper performance.
- Unplanned Capacity Adjustments. Here you can quantify unplanned resource allocations resulting from an incorrect estimation of the organization’s capacity.
- Resolution Time of Capacity Shortage: this is the response time that an organization has required to solve issues related to capacity planning. For example, the average time it has taken to hire skills that were not available.
Capacity planning as a continuous improvement process
Now that you know the steps you need to take to design a capacity planning process, you should know that not all the work is done yet. Capacity planning should be considered as a continuous improvement process, i.e., it should be monitored and reviewed from time to time to optimize it and eliminate bottlenecks that may arise.
Capacity planning process should be reviewed as it will become obsolete
It should also be reviewed so that the process itself does not become obsolete. We are in the era of change, in which customers and users are demanding new and increasingly innovative products and services that force companies to innovate in order not to lose market share.
That’s why planning capacity a year ahead doesn’t make much sense these days. Strategic objectives are evolving faster and faster, and organizations are required to cope with an ever-increasing volume of demand. In this context, it is recommended to plan capacity 3 to 6 months in advance so that a business can plan its capacity in a more efficient and agile way.
Capacity planning challenges
If you have followed the previous steps and have set up procedures for continuous improvement of the capacity planning process, everything will be advantageous and capacity planning will be aligned with your organization’s objectives.
However, if you omit some of the above steps, or have not done meticulous work in analyzing your resource pool or the current and future demand, then problems will arise. As we have already stated, this process is key to the correct performance of project portfolio management. So, the problems that will arise, whether you are a PMO manager, Program Manager, or Portfolio Manager, will be familiar to you.
These are the capacity planning challenges you may face if the process is not implemented in the right way:
- Overestimation of resource availability.
- A mismatch between skills and tasks to be carried out.
- Staff and teams overwhelmed by work overload.
- Customers and users unsatisfied.
- Process outdated after a short period of time.
1. Overestimation of resource availability
Description: for certain programs and projects you will not have the necessary resources or skills to undertake them successfully, which will cause barriers and bottlenecks in their execution.
Root cause: the analysis of the existing number of resources, which should have been done at the beginning of the capacity planning process, was not done in a detailed manner.
2. A mismatch between skills and tasks to be carried out
Description: Some programs and portfolios will not have the necessary skills to carry them out, or some of these skills will be duplicated, so the productivity of certain teams may be affected.
Root cause: as with the previous problem, a correct analysis of the skills available was not carried out.
3. Staff and teams overwhelmed by work overload
Description: This is one of the most common challenges in organizations that do not have efficient processes in place for Resource Management and Capacity Planning. Teams cannot cope with all the incoming demand, which has a negative impact on both budgets and delivery schedules for the projects and programs they manage, as well as on the morale of the company’s staff.
Root cause: There may be several causes of this issue:
- Failure to properly analyze the current and future demand.
- The number of resources and skills needed to meet this demand was not correctly estimated.
- No what-if scenario analyses have been performed prior to the planning of the allocation of resources to the different programs and portfolios.
- There are no efficient processes in the organization for tasks prioritization.
- No feedback loop from execution.
4. Customers and users unsatisfied
Description: The more barriers and bottlenecks arise in the capacity planning process, the more it will negatively impact business performance. And, consequently, the greater the frustration of customers and users for not receiving the value they expected.
Root cause: the capacity planning process in place is not efficient. It will have to be analyzed and audited to detect all the problems and solve them one by one.
5. Process outdated after a short period of time
Description: a few weeks or months after the process was implemented, some of the previously mentioned problems arise, coinciding with a change in the strategic positioning of the organization.
Root cause: capacity planning is probably being done a year ahead. In order to gain flexibility in reacting to these changes, it is recommended that capacity planning is done 3 to 6 months in advance.
Advantages of Capacity Planning
The solution to all these problems, as you can guess, is related to the continuous improvement processes that must be implemented in your capacity planning procedures.
This does not imply that other problems will not arise in the future (be sure that they will). But, at the end of the day, this process brings with it a number of benefits that will have a positive impact on the organization, from employee morale and motivation to the performance of the different projects, programs and portfolios you manage.
Capacity planning will positively impact organizational performance
These are the main advantages of capacity planning:
- Improved performance of your project portfolios.
- You avoid overloading your teams with initiatives that do not add value.
- Advanced management of your organization’s skills.
- Optimization of your resource allocation processes.
- Lower employee turnover rate.
1. Improved performance of your project portfolios
Being able to predict in advance whether the company has the resources and skills to undertake its project portfolios will make it possible to anticipate problems before they occur. This means:
- No more duplicate resources.
- No more resources that do not contribute any value to a given project or program.
Capacity planning also reduces downtimes or bottlenecks because of the absence of key resources and skills. This will increase the performance and success rate of your programs and project portfolios.
2. You avoid overloading your teams with initiatives that do not add value
By planning capacity and estimating in advance the different scenarios in which the organization may find itself in, you will be able to allocate your most valuable resources at any time to the initiatives that have the greatest strategic value for the business.
Those work environments that have capacity planning processes in place 3 to 6 months in advance are more agile in focusing their resources on continuous value delivery. The process itself encourages these resources to be dedicated to the initiatives that best fit their skills and, therefore, can be more productive.
3. Advanced management of your organization’s skills
By having listed the skills of your organization’s teams vs. the skills needed to successfully deliver your portfolios of projects and products, you will be able to anticipate the obstacles and bottlenecks of resource management, which are:
- Not having the relevant skills to successfully undertake strategic initiatives in your organization.
- The duplicity of resources and skills in certain teams and projects.
- Managers block the allocation of resources to certain projects.
Capacity planning will positively impact organizational performance
4. Optimization of your resource allocation processes
You will be able to plan resource allocation several months in advance. This will enable PMO and resource managers:
- Negotiate in advance with the managers of the different departments about the allocation of resources to the projects you are working on without compromising the day-to-day operations of those teams.
- Forecast the total number of hours that resources will spend on the projects in which they will be involved.
- Reduce downtime of your most valuable resources.
5. Lower employee turnover rate
Capacity planning processes have a very positive impact on employee morale and commitment to the organization’s mission and vision. Because resources can be allocated to the initiatives that best match your skills and knowledge, you will achieve:
- Higher quality and performance rates of your project and product portfolios.
- A lower employee turnover rate.
- Longer retention in the organization of your most valuable resources.
Capacity planning best practices
To summarize, capacity planning is a comprehensive continuous improvement process that, when well designed and implemented, will take resource allocation and resource management in your organization to the next level. However, for the process to work, you must rely on a series of tips and best practices that will make its implementation smoother.
These are some of the best practices for capacity planning:
- Prioritize your projects, programs and portfolios based on strategy.
- Get a complete and detailed view of the demand.
- List your current capacity.
- Consider capacity planning as a continuous improvement process.
- Use PPM software with What-if scenario analysis capabilities.
Capacity planning examples in a PPM software
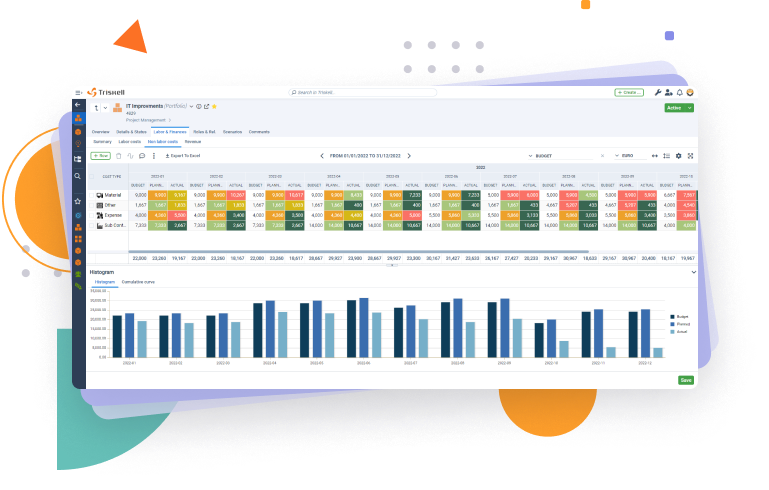
Having a PPM tool like Triskell, with functionalities for Resource Management and Capacity Planning will be your best support to get the process up and running and optimize it.
With Triskell you will go one step beyond traditional Resource Management at the project level. From our platform you will be able to:
- Manage the existing capacity available in your organization.
- Align Resource Management with demand planning and your strategic objectives.
Here are some examples of capacity planning and resource management functionalities that you will find in Triskell’s platform:
- What-if Scenario Analysis features so you can plan in advance the portfolios of projects and products most relevant to the organization and the capacity required to successfully carry out these initiatives.
- Gantt charts to visualize the use of resources at project, program or portfolio level, and also to detect problems of over-allocation or lack of resources.
- Timesheets with which staff can record time spent on both project and non-project-related activities.
Conclusion: Capacity planning will have a major impact on the success of your organization
Hopefully this post has helped you understand that proper capacity planning will help your business meet its strategic objectives while optimizing the performance of your project and product portfolios.
It is a process that cannot be managed with a simple spreadsheet because of all the stakeholders and data involved. Therefore, and following the last tip we have provided in the previous section, you should implement a PPM solution such as Triskell, which has functionalities for Resource Management that will help you to plan, manage and allocate resources in a much more efficient way.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get stories like this in your inbox
Request a demo of Triskell Software
Do you think Triskell Software is the solution you need to take your organization’s resource management to excellence? If so, request a demo of Triskell.
FAQs about capacity planning
What is the goal of capacity planning?
The goal of capacity planning is to ensure you have the right resources available to meet your project’s needs, when you need them.
This includes having the right people with the necessary skills available at the right time, but can also encompass tools and equipment.
How can you get started with capacity planning?
There are a few ways to get started with capacity planning. You can use specific software designed for this purpose, or you can utilize templates that are available online.
No matter which method you choose, the key is to understand your team’s capabilities and workload.
What are the benefits of capacity planning?
Capacity planning offers a number of advantages including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
By ensuring you have the right resources in place, you can avoid overcommitting your team and potentially missing deadlines.
Additionally, capacity planning can help you identify areas for improvement and growth within yours teams.
Related Content

6 time-consuming activities PMOs will leave behind with a PPM tool
Boost Productivity NOW! Top time-Consuming activities PMOs MUST ditch TODAY! Say goodbye to waste! Learn More.

Project Management vs Project Portfolio Management: understanding the differences
Explore the intricacies of Project Management (PM) and Project Portfolio Management (PPM) in this comprehensive guide.

The ultimate guide to create a Strategic PMO for impactful PPM
In this post, we will show you the key roles and responsibilities of a strategic PMO, as well as the essential components and best practices for its success.
